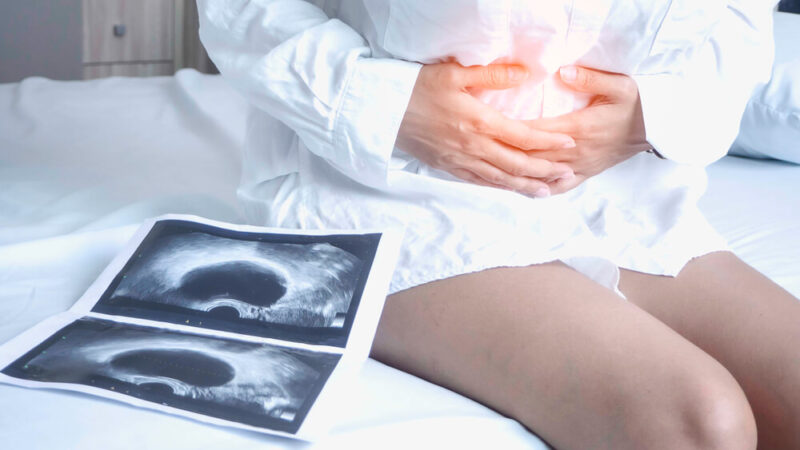
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets within or on the surface of an ovary. Women have two ovaries — each about the size and shape of an almond — on each side of the uterus. Eggs (ova), which develop and mature in the ovaries, are released in monthly cycles during the childbearing years.
Many women have ovarian cysts at some time. Most ovarian cysts present little or no discomfort and are harmless. The majority disappear without treatment within a few months.
However, ovarian cysts — especially those that have ruptured — can cause serious symptoms. To protect your health, get regular pelvic exams and know the symptoms that can signal a potentially serious problem.
Symptoms Overview
The presence of ovarian cysts often goes unnoticed as they rarely cause symptoms. However, when they do, the symptoms can be varied and depend on the size, type, and if there’s any complication associated with the cyst.
Pain and Discomfort
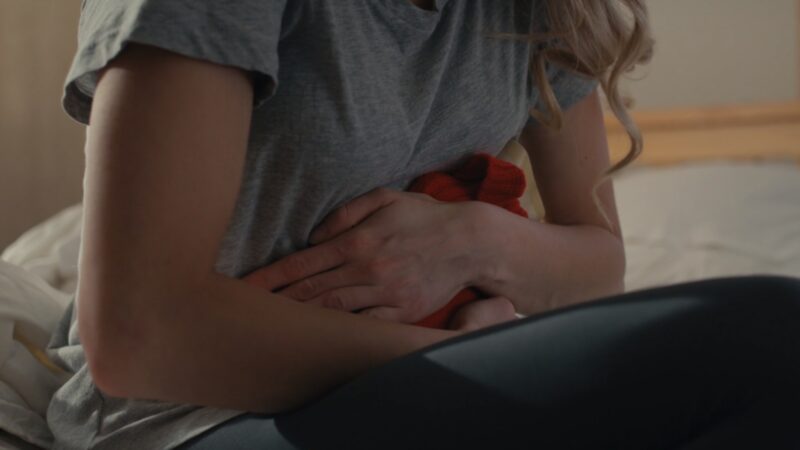

One of the most common symptoms of ovarian cysts is pain or discomfort in the abdomen. This pain can be sharp or dull and may come and go. It often occurs in the lower abdomen and can radiate to the lower back or thighs. The pain may be more noticeable during certain activities, such as exercise, sexual intercourse, or during your menstrual period.
Menstrual Irregularities
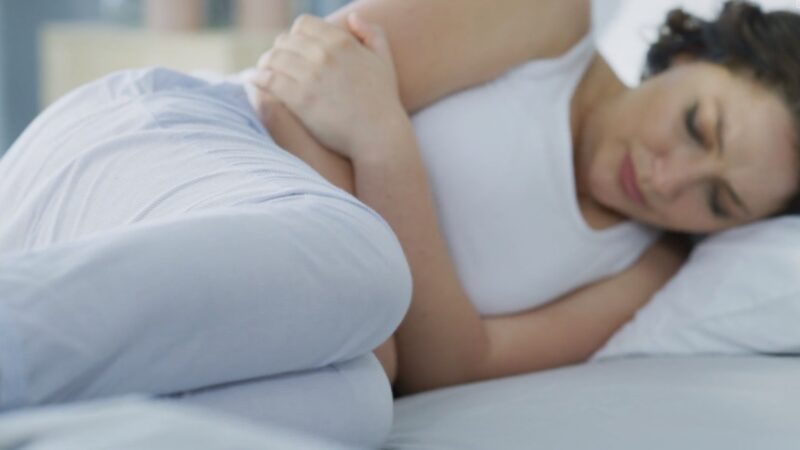

Ovarian cysts can sometimes cause menstrual irregularities. This can include delayed, irregular, or unusually heavy or light periods. In some cases, women might experience spotting or bleeding outside of their regular menstrual cycle.
Bloating and Swelling
A feeling of fullness or heaviness in the abdomen is another symptom associated with ovarian cysts. This can lead to bloating, swelling, and sometimes an increase in abdominal size. This symptom is often more pronounced as the cyst grows in size.
Pelvic Pain during Intimacy
Pain during sexual intercourse, known as dyspareunia, can be a symptom of an ovarian cyst. This pain is usually felt deep in the pelvis and may be more pronounced on the side where the cyst is located.
Urinary and Bowel Symptoms
Larger cysts may press against the bladder and bowel, leading to urinary and bowel symptoms. These can include an increased urge to urinate, difficulty emptying the bladder, or pain during bowel movements.
Nausea and Vomiting

In some cases, particularly when a cyst is large or has ruptured, nausea and vomiting may occur. This symptom is less common but can be indicative of a more severe condition, such as torsion or rupture of the cyst.
Recognizing Complications
While most ovarian cysts are benign and resolve on their own, complications can occur. Ovarian torsion, where the ovary gets twisted due to a large cyst, can lead to severe pain and requires immediate medical attention. Similarly, a ruptured cyst can cause intense pain and internal bleeding. These situations are medical emergencies.
Diagnosis and Medical Attention
If you experience any symptoms of an ovarian cyst, especially severe abdominal pain, fever, or rapid breathing, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis is key in managing the symptoms and preventing complications. Doctors often use a combination of physical examinations, ultrasound, and sometimes blood tests to diagnose ovarian cysts.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for ovarian cysts depends on the size, type, and symptoms. Small, asymptomatic cysts may not require treatment and are often monitored with regular ultrasounds. In contrast, larger or symptomatic cysts may require medication or surgery. Birth control pills are sometimes prescribed to prevent the formation of new cysts.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatment, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage the symptoms of ovarian cysts. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management techniques can be beneficial. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also help alleviate discomfort.
FAQs
Can ovarian cysts lead to cancer?
Ovarian cysts are mostly benign and do not lead to cancer. However, in rare cases, some cysts, particularly those that persist and grow larger, can be malignant. It’s important to have regular check-ups and ultrasounds to monitor any changes in the cysts that might indicate a more serious condition.
Are there lifestyle factors that can reduce the risk of developing ovarian cysts?
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent ovarian cysts, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can be beneficial. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, managing stress, and avoiding excessive hormonal fluctuations. Additionally, regular gynecological exams can help in early detection and management.
How do ovarian cysts affect fertility?
Most ovarian cysts, especially functional cysts that occur during the menstrual cycle, do not affect fertility. However, certain types of cysts, such as endometriomas or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can impact a woman’s ability to conceive. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for specific concerns about fertility.
Can ovarian cysts recur after treatment?
Yes, ovarian cysts can recur after treatment, especially in women who are in their reproductive years. The recurrence rate depends on the type of cyst and the treatment method. Women are often advised to have regular follow-ups to monitor for any new cyst development.
Is surgery always necessary for treating ovarian cysts?
Surgery is not always necessary for ovarian cysts. It is generally reserved for cysts that are large, do not go away on their own, or appear suspicious on ultrasound. The decision for surgery also depends on the patient’s age, symptoms, and whether they have completed childbearing.
Can menopause affect the occurrence of ovarian cysts?
The occurrence of functional ovarian cysts typically decreases after menopause because these cysts are related to ovulation, which ceases after menopause. However, postmenopausal women can still develop cysts, and any cyst after menopause is more closely monitored due to a higher risk of malignancy.
Final Words
Ovarian cysts are a common health issue for women. While they often go unnoticed and resolve on their own, it’s important to be aware of the symptoms that can indicate a larger or more problematic cyst. Regular pelvic exams and being attentive to changes in your body are key to early detection and treatment. If you have concerns or experience any unusual symptoms, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for advice and treatment options.