As women, our reproductive health is a crucial aspect of our overall well-being, and understanding conditions that can affect it is essential. Dermoid ovarian cysts are a type of benign tumor that can develop in a woman’s ovaries.
They are unique in that they can contain a variety of different types of tissues, including hair, skin, and even teeth. In this article, we’ll explore these cysts, shedding light on their origins, potential effects, and the available treatment options.
What Are They?

Dermoid cysts are essentially sac-like growths on the ovaries that are filled with various types of tissues. They can range in size from as small as a pea to larger than a grapefruit. While they are benign and not cancerous, they can cause complications.
Prevalence
These cysts are most commonly found in women in their reproductive years, typically between the ages of 20 and 40. However, they can occur at any age, even in fetuses.
It’s estimated that about 10-20% of women will develop a dermoid cyst at some point in their lives.
| Age Group | Occurrence of Dermoid Cysts |
|---|---|
| Reproductive Years | Most Common (20 – 40 years) |
| Adolescents | Possible but Less Common |
| Children | Rare and Occasional |
| Fetus | Occasional, Detected Prenatally |
Causes of Dermoid Ovarian Cysts
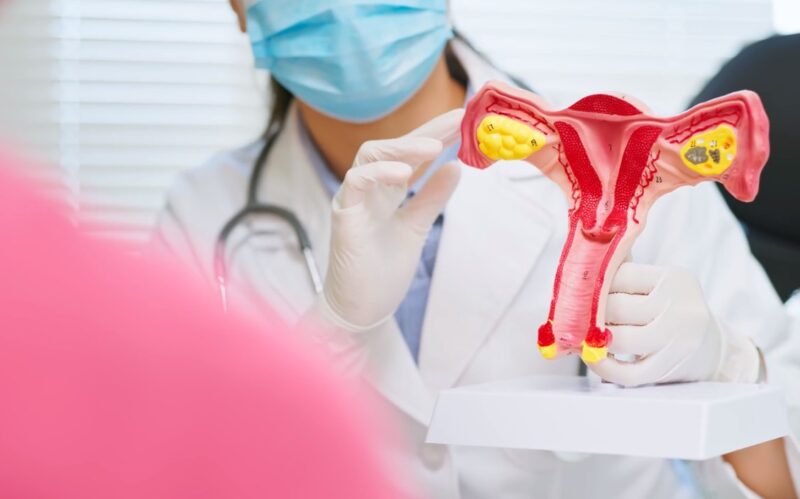
Understanding the root causes of these cysts can help in their prevention and management. While the exact cause is still a subject of research, several theories exist.
Embryonic Cell Growth
One of the leading theories is that dermoid cysts arise from embryonic cells. These cells are present from birth and have the potential to develop into any type of tissue. Over time, these cells can grow and form a cyst, which can then fill with various types of tissues.
Genetic Factors
While most dermoid cysts are not hereditary, there is some evidence to suggest that genetics may play a role. Some families seem to have a higher prevalence of these cysts, suggesting a possible genetic link.
However, more research is needed to confirm this theory.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Many women with dermoid cysts may not even realize they have one, as they often don’t cause symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can be quite varied.
Common Symptoms
The most common symptom of a dermoid cyst is pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen. This can be due to the cyst itself or complications like rupture or torsion. Other symptoms can include bloating, irregular periods, and pain during intercourse.
Diagnostic Procedures
If a dermoid cyst is suspected, a doctor will typically order an ultrasound to visualize the cyst. This imaging test can often identify the cyst’s unique characteristics, such as its solid components or the presence of hair or teeth.
In some cases, an MRI or CT scan may be needed for a clearer view.
Possible Complications

While these cysts are benign, they can lead to complications if not addressed. These complications can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and other health concerns.
Rupture and Torsion
The two most common complications are rupture and torsion. A rupture occurs when the cyst breaks open, releasing its contents into the body. This can cause pain, inflammation, and even infection.
Torsion, on the other hand, happens when the cyst twists on itself, cutting off its blood supply. This can be extremely painful and requires immediate medical attention.
Potential for Malignancy
While rare, there is a small chance that a dermoid cyst can become malignant or cancerous. This risk increases with age, especially after menopause. It’s essential to monitor any ovarian cyst for changes and to have regular check-ups with a gynecologist.
Treatment Options

When it comes to treating dermoid ovarian cysts, the approach largely depends on the size, location, and any associated symptoms or complications.
Observation and Monitoring
For smaller cysts that aren’t causing symptoms, a watch-and-wait approach might be recommended. This involves regular ultrasounds to monitor the cyst’s size and characteristics. If the cyst remains stable and doesn’t grow or change, no further treatment might be necessary.
Medication
While medications can’t cure dermoid cysts, they can help manage symptoms. Pain relievers, for instance, can alleviate discomfort. Birth control pills might be prescribed to prevent the formation of new cysts, though they won’t shrink existing ones.
Surgical Interventions
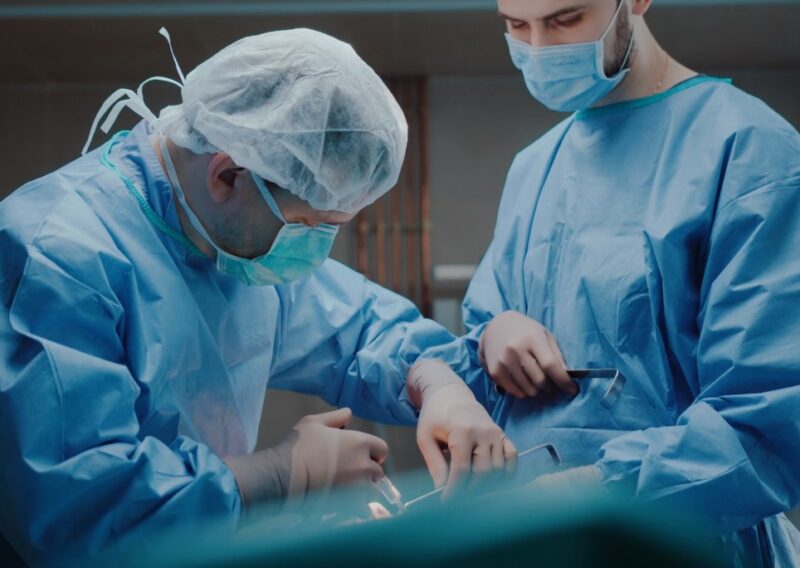
In cases where the cyst is large, causing symptoms, or showing signs of complications, surgery might be recommended.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses small incisions and a camera to remove the cyst. It’s often the preferred method for smaller cysts and offers a quicker recovery time compared to traditional surgery.
Laparotomy
For larger cysts or if there’s a concern about cancer, a laparotomy might be performed. This involves a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the cyst. The recovery time is generally longer than with laparoscopy.
Post-Treatment Care and Recovery

After treatment, especially surgery, it’s crucial to follow post-care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery and prevent complications.
Recovery Timeline
The recovery timeline largely depends on the type of treatment received. For laparoscopy, most women can return to their normal activities within a week. However, for a laparotomy, the recovery might take several weeks.
Follow-up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor healing and ensure that the cyst hasn’t returned. These appointments typically involve physical exams and ultrasounds. It’s also a chance to discuss any concerns or symptoms with the doctor.
Prevention and Lifestyle Adjustments

While it’s challenging to prevent dermoid cysts entirely, certain lifestyle adjustments can help reduce the risk and manage symptoms.
Regular Check-ups
Having regular gynecological exams can help detect and monitor any ovarian cysts. Early detection can prevent complications and allow for more treatment options.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and adopting a balanced diet can support overall ovarian health. While these measures might not prevent dermoid cysts directly, they can help in managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
FAQs:
Are dermoid cysts painful?
Most don’t cause symptoms unless they’re especially large. However, they can cause pain and pressure in the abdomen.
What happens if a dermoid cyst ruptures?
The cyst can leak its contents into the abdominal cavity. While the body often absorbs the contents without issues, it can sometimes lead to infections requiring emergency medical attention.
How fast do they grow?
They grow slowly, with most growth occurring during reproductive years.
Can I reduce my risk of an ovarian dermoid cyst?
No, they form before birth.
Do they go away without treatment?
No, they remain unless removed.
The Bottom Line
Dermoid ovarian cysts, though benign, are a significant concern for many women. Their mysterious origin, varied symptoms, and potential complications make them a topic of interest in women’s health.
It’s always essential to prioritize regular check-ups and maintain open communication with healthcare professionals when it comes to any aspect of your well-being, including this one. Knowledge, vigilance, and proactive care are the cornerstones of managing and living with these cysts.

