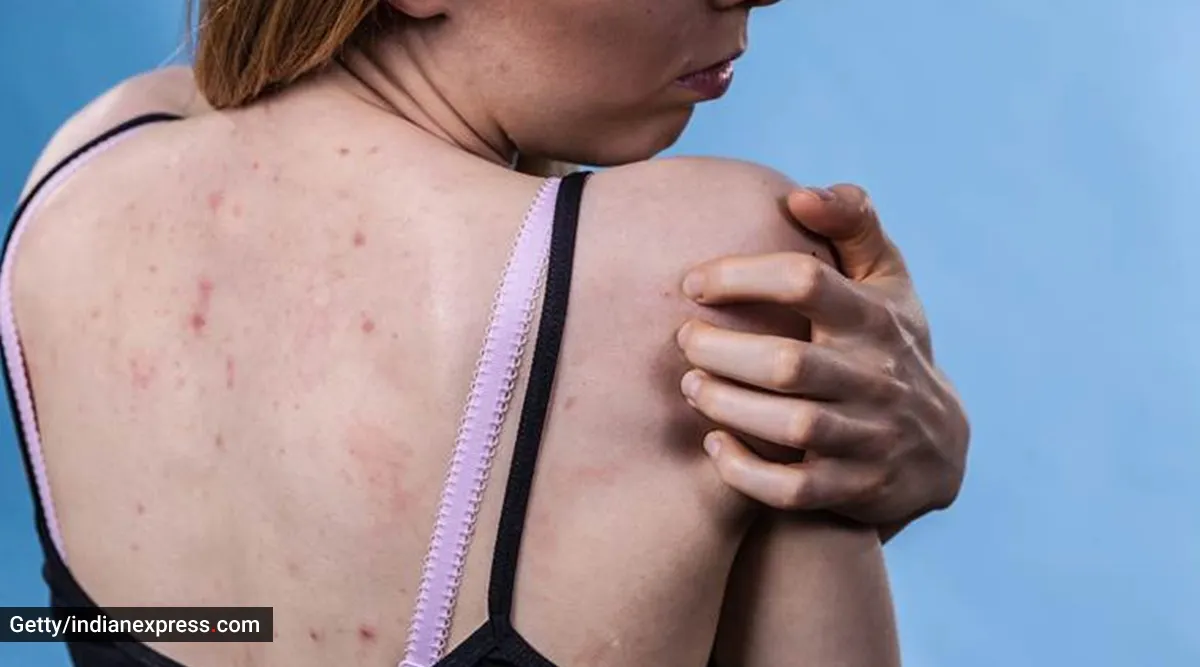
Pustules, a type of acne, present as red bumps with white, pus-filled centers. They are larger than whiteheads and blackheads and can appear on various parts of the body. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the causes, appearance, and treatment of pustules, providing valuable insights for effective management.
What Causes Pustules?
A clogged pore is the root cause of a pustule. Oil, bacteria, or dead skin can block the pore, leading to the formation of pustules. These occur when the walls of the affected pore begin to break down, resulting in a larger size than whiteheads and blackheads.
Acne and folliculitis are common causes of pustules. However, they can also occur in people with certain types of psoriasis, like palmoplantar pustulosis, and some forms of eczema, such as dyshidrotic eczema.
Pustules contain pus as the body fights against dirt or bacteria. Pus is mostly dead white blood cells, a natural product of the immune system.
Where Do They Occur?
Pustules can appear anywhere but are more common in oily areas like the face, neck, and areas prone to sweat like armpits, chest, and pubic area.
Common areas for pustules include:
- Face
- Neck
- Chest
- Underarms
- Hairline
- Back
- Shoulders
- Pubic area
Pustule vs. Other Types of Pimple
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, pimples can be classified into six types: whiteheads, blackheads, pustules, papules, nodules, and cysts. Pustules are typically white and tender, containing pus, unlike papules.
Blackheads have open pores, while whiteheads have closed pores. Papules and pustules are larger than blackheads and whiteheads. Nodules and cysts, larger still, may need medical attention.
Treatment
Home Remedies and OTC Treatments
Small pustules can heal on their own, but treatments and home remedies can speed up the process. Keeping the skin clean and oil-free is crucial. This can be achieved by washing with warm water and mild soap twice a day.
OTC treatments helpful for pustules include:
- Salicylic acid
- Sulfur
- Peroxide
However, avoid using these near the genitals and picking at or popping a pustule.
If home remedies fail, consult a doctor for prescription treatments. Remember, acne products can dry out the skin. If irritation occurs, discontinue use.
Home Remedies
Several home treatments are effective for pustules:
- Clay masks: Draw oil and dirt from the skin.
- Essential oils: Tea tree or rosemary oil for anti-inflammatory effects.
- Aloe vera gel: Offers antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Prevention
To prevent pustules, clean the skin prone to pimples and keep it oil-free. This should be done at least twice a day using a mild soap. Avoid products containing oils, like certain moisturizers and sunscreens, as they can clog pores.
Outlook
Pustules are generally harmless and often resolve independently. Preventive measures and OTC treatments can be effective. If pustules worsen, don’t clear up, or are chronic, consult a doctor for additional treatment options.
Managing Pustules Effectively
Lifestyle and dietary factors play a significant role in managing pustules. Simple changes can significantly impact the frequency and severity of breakouts. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and reducing stress.
Key lifestyle changes include:
- Consuming a diet low in sugar and dairy.
- Increasing intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular exercise to improve blood circulation and reduce stress.
Skin Care Routine
A consistent skincare routine is crucial in managing pustules. Gentle cleansing, proper hydration, and avoiding harsh skin treatments are key components of an effective routine.
Important skincare tips:
- Use non-comedogenic products that won’t clog pores.
- Avoid excessive scrubbing or touching the face.
- Regularly clean items that touch your face, like phone screens and pillowcases.
Regular Dermatologist Visits
Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can provide personalized care. They can monitor your skin’s condition, adjust treatments as necessary, and offer professional advice on skincare products.
Advanced Treatment Options
For severe or persistent pustules, prescription medications can be effective. According to the Mayo Clinic, options include topical retinoids, antibiotics, and hormonal treatments for women. These treatments target different acne causes, from reducing oil production to fighting bacterial infections.
In-Office Procedures
In severe cases, dermatologists may recommend in-office procedures. These include:
- Light therapy: Kills bacteria and reduces inflammation.
- Chemical peels: Removes dead skin cells, promoting new skin growth.
- Drainage and extraction: Removes large pustules and cysts.
Myths and Misconceptions
Misconceptions about acne can lead to ineffective or harmful treatments. It’s important to recognize these myths:
- Myth: Acne is caused by dirty skin.
- Reality: Acne is caused by a combination of factors, not just cleanliness.
- Myth: Only teenagers get acne.
- Reality: Acne can affect people of all ages.
- Myth: Popping pimples will make them go away faster.
- Reality: Popping pimples can cause scarring and spread bacteria.
FAQ
Can diet affect acne pustules?
Yes, certain foods can exacerbate acne. Diets high in sugar and dairy are often linked to increased breakouts.
Is it safe to use makeup on acne pustules?
Yes, but choose non-comedogenic makeup that won’t clog pores. Always remove makeup before bed.
Can stress cause acne pustules?
Stress doesn’t directly cause acne but can aggravate it by triggering hormonal changes.
Are natural remedies effective for pustules?
Some natural remedies can be effective, but it’s important to patch test and consult a dermatologist.
How long does it take for a pustule to heal?
Healing time varies, but with proper treatment, pustules typically improve within a few days to a week.
Can pustules leave scars?
If not properly treated, pustules can leave scars. Avoid picking or popping them to reduce this risk.
Are pustules contagious?
No, acne pustules are not contagious. They result from internal factors like hormones and oil production.
Conclusion
Understanding, preventing, and treating acne pustules require a comprehensive approach that includes skincare, lifestyle changes, and possibly medical interventions. By debunking myths and following expert advice, individuals can effectively manage their acne and improve their skin health. Remember, patience and consistency are key in achieving clear skin.