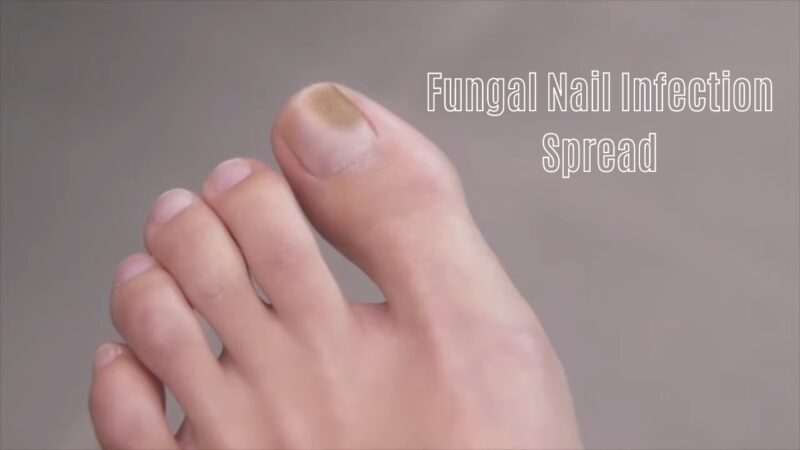
Fungal infections are a prevalent issue affecting many individuals. They involve a change in the appearance and texture of the nails, often leading to discomfort and aesthetic concerns.
While these infections can occur in various settings, they are generally manageable with proper care and attention. The specifics of prevention and treatment vary, but maintaining good hygiene plays a fundamental role in addressing this condition.
Key Takeaway:
- Fungal infections can spread from one nail to another, from the feet to the hands or vice versa, and can also be transmitted to other individuals through direct contact or shared surfaces, especially in warm, moist environments.
- To avoid fungal infections, maintain good foot hygiene, keep them trimmed and clean, avoid walking barefoot in public places, and refrain from sharing personal grooming tools.
Definition and Causes
Fungal infections, medically known as onychomycosis, are infections of the nail bed and plate caused by various fungi, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds. These infections typically occur when fungi invade the nail through a small trauma or separation between the nail and skin, thriving in warm, moist environments like shoes, socks, and public areas such as swimming pools and locker rooms.
Types of Fungal Nail Infections
Fungal infections are one of the most common transmittable skin infections and they can be classified into several types based on the fungus involved:
- Distal Subungual Onychomycosis (DSO): The most common type, caused primarily by dermatophytes. It starts under the nail at the tip and spreads toward the cuticle. It causes it to be yellow, thick, and crumbly.
- White Superficial Onychomycosis (WSO): This type affects the top layer of the nail, starting with white spots that spread over the nail’s surface, making it rough and crumbly.
- Proximal Subungual Onychomycosis (PSO): Less common, it starts at the cuticle and spreads toward the tip. This type is more prevalent in individuals with a compromised immune system.
- Candidal Onychomycosis: Caused by Candida yeasts, this type can affect its plate and surrounding skin, leading to discoloration, thickening, and painful swelling of the surrounding skin.
- Endonyx Onychomycosis (EO): A rare type where the nail plate gets infected with a fungus, leading to a milky white discoloration without the nail thickening or separating from the bed.
Common symptoms and signs include:
- Discoloration (they turn white, yellow, brown, or green)
- Thickening
- Brittleness, resulting in crumbly or ragged edges
- Change in shape or distortion
- A dark color building up under the nail due to debris
- A slight foul odor
- Separation
- Overall discomfort or pain in the affected area, especially when wearing shoes or applying pressure.
Transmission of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections can spread from one to another through direct contact with the fungal spores. This can happen when an infected one comes into contact with another one or the skin surrounding it, often facilitated by minor injuries, cuts, or openings. The spread is more likely in warm, moist conditions where fungi thrive, such as when feet are confined within tight, unventilated shoes.
The infections can also spread from person to person, especially in communal settings like gyms, swimming pools, and shower rooms, where individuals walk barefoot. Sharing personal items like towels, clippers, and socks can also facilitate the transfer of fungal spores.
Individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing foot problems are more susceptible to contracting infections from others.
Risk Factors
Infections can happen to everyone, however some sensitive groups can be more affected. Factors may include:
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Older individuals are more susceptible due to reduced blood circulation, slower nail growth, and more years of exposure to fungi. |
| Heavy sweating | A humid environment around your feet can foster fungal growth. |
| History of athlete’s foot | Infections can spread from the skin to the nails. |
| Walking barefoot in damp communal areas | Places like swimming pools, gyms, and shower rooms are breeding grounds for fungi. |
| Minor skin injuries | Cuts or abrasions can make it easier for fungal infections to take root. |
| Poor circulation | Conditions like diabetes can reduce blood flow to the feet, increasing susceptibility to infections. |
| Weak immune system | People with compromised immune systems, from medications or conditions like HIV, are more at risk. |
| Living with someone with a fungal infection | Fungi can spread from person to person within a household. |
Health Issues Caused by Fungal Nail Infections:
While primarily affecting the nails’ appearance, if left untreated, fungal infections can lead to more serious health issues, particularly for individuals with diabetes or weakened immune systems:
- Pain and discomfort: As it thickens and deforms, it can make walking, standing, or wearing shoes painful.
- Spread of infection: The infection can spread beyond the nail to the skin, causing athlete’s foot, or to other parts of the body, like the groin or scalp.
- Secondary bacterial infections: Cracks or cuts in the skin caused by fungal infections can allow bacteria to enter, leading to further complications.
- Foot ulcers: People with diabetes might develop foot ulcers from minor foot injuries due to altered sensation.
- Impaired mobility: Severe infections can lead to difficulty walking or operating normal daily activities, impacting quality of life.
Prevention Techniques
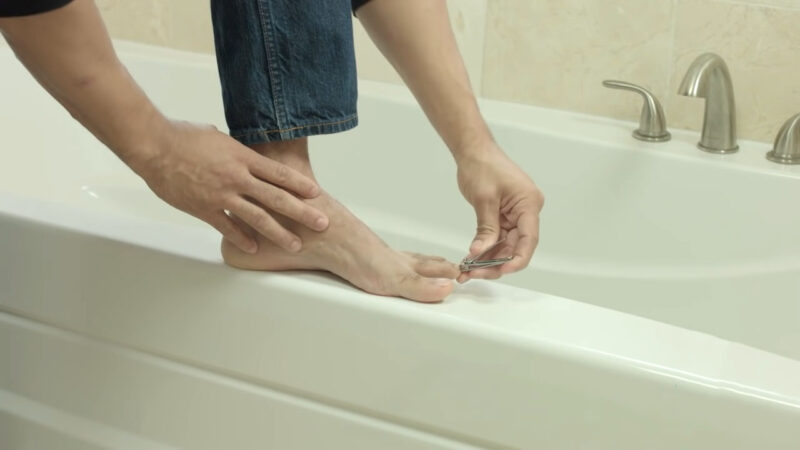

Preventing fungal infections begins with maintaining good foot hygiene. This means washing your feet regularly with soap and water and thoroughly drying them afterward, especially between the toes where moisture can accumulate. Using antifungal powders or sprays on your feet and inside your shoes can help reduce moisture and prevent the growth of fungi.
Wearing breathable footwear is also crucial in preventing fungal infections. Shoes made of materials that allow air to circulate can help keep your feet dry. If you tend to sweat a lot, changing your socks twice a day can also be beneficial.
Keeping your nails trimmed is another key preventive measure. They should be cut straight across and filed down thickened areas. Avoid cutting them too short or rounding the corners to prevent ingrown toenails, which can increase the risk of fungal infections.
When visiting salons, ensure they properly sterilize their instruments to avoid the transmission of fungal infections during manicures or pedicures. By adopting these practices, you can significantly lower your chances of developing fungal infections.
Treatment Options
Treatment for fungal infections varies depending on the severity and type of the infection. Here are some common approaches:
Topical Treatments
These are applied directly to the infected nail and surrounding skin. Over-the-counter antifungal creams and ointments are available, but prescription topical treatments are generally more effective. They require diligent application over a period, often several months, as they grow out.
Oral Antifungal Medications
For more severe or persistent cases, doctors may prescribe oral antifungal drugs. These medications can help a new nail grow free of infection, slowly replacing the infected part. They are usually taken for 6 to 12 weeks but it can take four months or longer to eliminate an infection.
Medicated Polish
A prescription antifungal polish called ciclopirox is an option. It’s painted on the infected nails and surrounding skin once a day. After seven days, the layers of polish are wiped off with alcohol, and fresh applications are started. This treatment can take a year or longer to clear up an infection.
Medicated Creams
Your doctor may prescribe an antifungal cream, which is rubbed into your infected nails after soaking. These are often used in conjunction with other treatments.
Laser and Photodynamic Therapy
Some clinical studies suggest that laser and light-based therapies can be effective in treating fungal infections by inhibiting fungal growth. However, these treatments are usually more expensive and may not be widely available.
Nail Removal
If the infection is severe or extremely painful, removing the nail might be an option. A new one will usually grow in its place, but it might take a year or longer. In some cases, the infection can recur after it grows back.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
While less effective for treating fungal infections, improving hygiene and regularly cleaning and drying feet can help limit the spread of the infection. Some people also use home remedies like tea tree oil or vinegar soaks, but their effectiveness is less clear, and they are not a substitute for medical treatment.
Complications and Consequences

Untreated fungal infections can lead to several complications and consequences. Over time, the infection can cause permanent damage to the nails, leading to their distortion, discoloration, and detachment. This can result in pain and difficulty walking or wearing shoes, significantly impacting daily activities and quality of life.
Infections can spread beyond the nail to the skin, causing athlete’s foot, or even to other parts of the body, which is particularly concerning for individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying conditions like diabetes.
In such cases, the infection can lead to more severe outcomes, including bacterial infections, cellulitis, and foot ulcers, necessitating more intensive treatment and, in extreme cases, leading to limb amputation.
FAQs
Can I get a fungal infection from a pedicure?
Yes, if the tools are not properly sterilized, you can contract a fungal nail infection from a pedicure.
Will wearing nail polish worsen a fungal infection?
Wearing nail polish can trap moisture and worsen a fungal infection, making it harder to treat.
Can fungal infections lead to loss of the nail?
In severe cases, fungal infections can lead to the loss of the nail.
Are fungal infections contagious to family members?
Yes, fungal infections can spread to family members through shared surfaces and personal items.
Can I treat a fungal nail infection with over-the-counter products?
Over-the-counter products can be used for mild cases, but severe infections typically require prescription medication.
Conclusion
Fungal nail infections, while common, can lead to significant discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. Understanding the risk factors, and transmission mechanisms, and implementing preventive measures are crucial steps in avoiding these infections.
Should you suspect a fungal infection, it’s important to seek treatment early to prevent the spread and worsening of the condition.
You can effectively manage and overcome the infection with the right approach, including hygiene practices, proper footwear, and medical treatment when necessary. Remember, your feet are foundational to your overall health and well-being, so give them the care and attention they deserve.